A Complete Overview of Automotive Steering Systems: Structure, Working Principles, and EPS/EHPS Technologies
1. Steering System Structure and Operating Principles
1.1 Steering System Structure
- Steering Control Mechanism: This includes the steering wheel, steering column, and the two tie rods connecting them. These components allow the driver to apply steering input to the vehicle.
- Steering Gear (Steering Mechanism): As the core of the steering system, the steering gear amplifies the driver’s input force and changes the direction of force transmission. Common types include rack-and-pinion, recirculating ball, and worm-crank designs.
- Steering Linkage: A series of rods and mechanical linkages between the steering gear and the steering knuckles. Their role is to transfer output force from the steering gear to the steering knuckle, enabling wheel angle changes while maintaining correct steering geometry.
- Power-Assist Systems: Systems such as electro-hydraulic power steering (EHPS) and electric power steering (EPS) use electronic control of hydraulic pumps or electric motors to provide steering assist, improving steering ease and driving comfort.
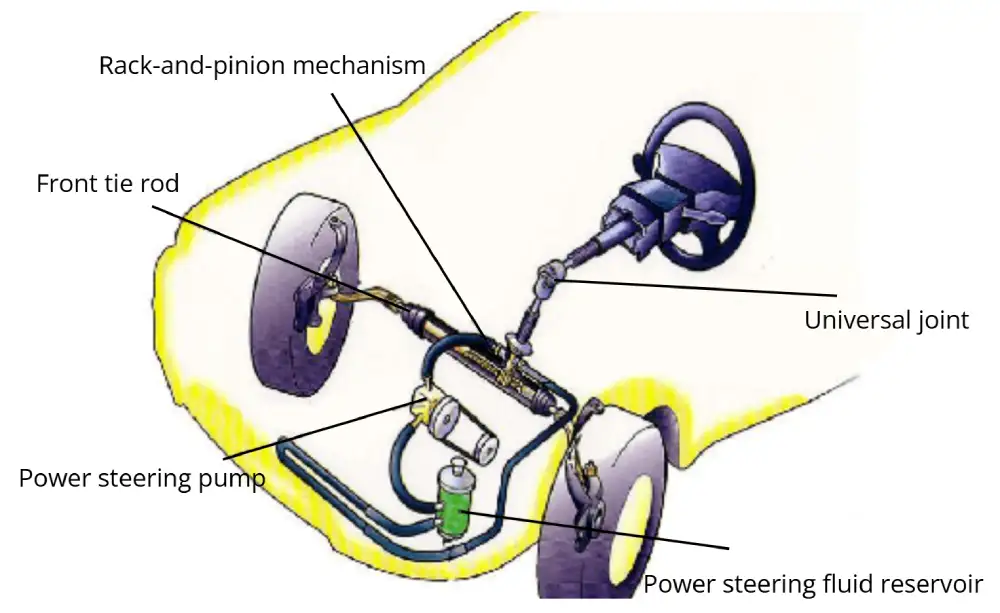
1.2 Operating Principle of the Steering System
Using a rack-and-pinion system as an example:
- The steering wheel is connected to the steering column, so turning the wheel rotates the column.
- Through the steering intermediate shaft and joints, torque is transmitted to the input shaft of the steering gear.
- The rack-and-pinion mechanism converts the rotational input into linear (or near-linear) motion, pushing or pulling the steering linkage and steering knuckle, causing the front wheels to steer.
The rack-and-pinion steering gear reduces speed and increases torque while converting rotational motion into linear motion.
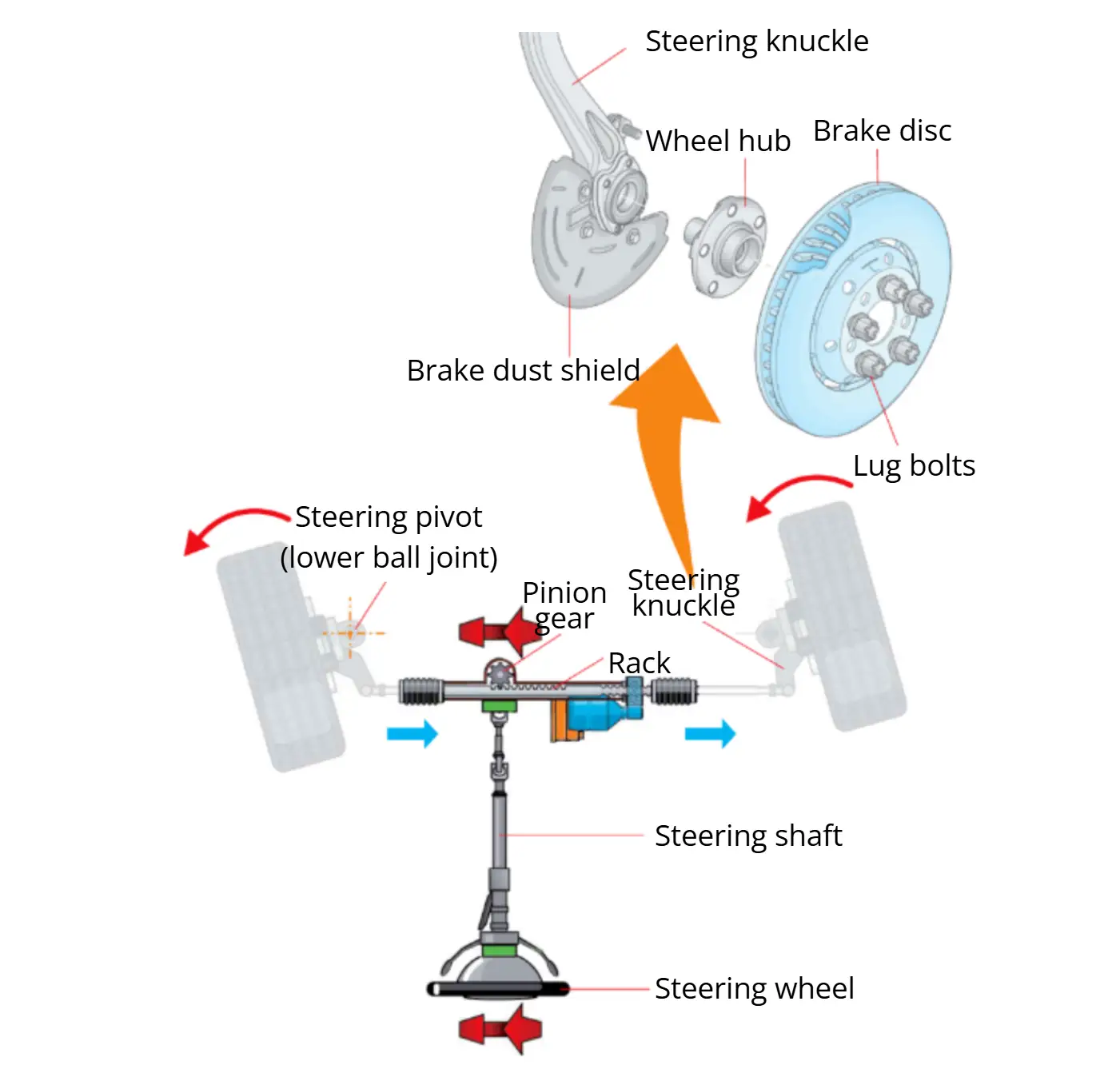
2. Types of Steering Systems
2.1 Mechanical Steering Systems
Mechanical steering linkages connect the steering gear to the wheels and transfer steering force to the knuckles while maintaining proper steering geometry.
2.2 Hydraulic Power Steering (HPS)
Hydraulic power steering reduces steering effort and absorbs road shocks. The key feature of a hydraulic power steering system is that the power steering pump is driven either by the engine’s accessory belt or by an electric motor. The pump delivers pressurized steering fluid to the steering control valve, which regulates the pressure and directs the flow. The fluid is then routed to one side of the hydraulic cylinder inside the steering gear, where it generates the assist force that drives the rack-and-pinion mechanism.
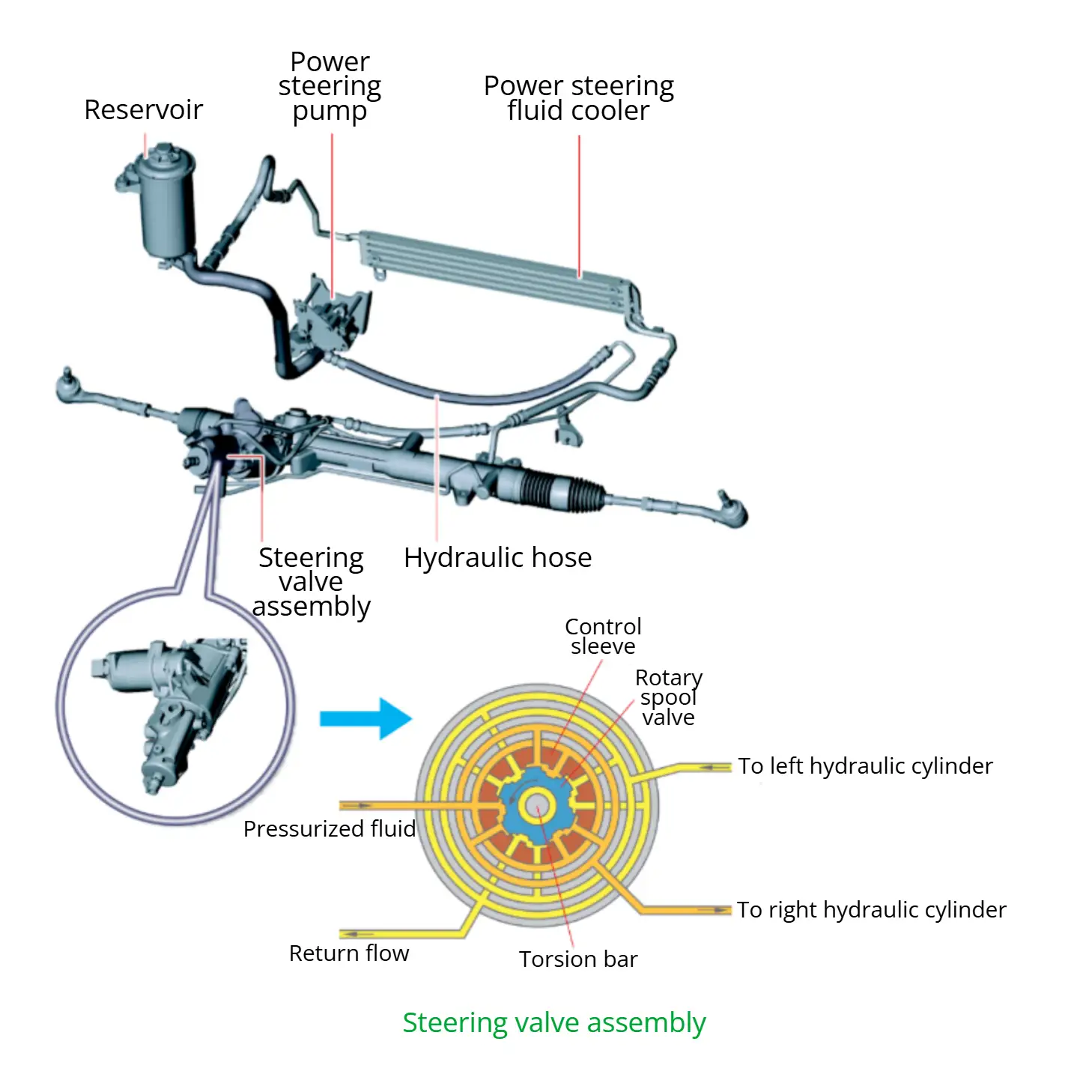
2.3 Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering (EHPS)
EHPS systems solve the drawbacks of traditional HPS. Instead of being driven by the engine belt, the hydraulic pump is driven by an electric motor. An electronic control unit (ECU) adjusts the motor speed and hydraulic flow based on vehicle speed and steering angle velocity. This enables continuously adjustable assist torque to suit both low-speed maneuvering and high-speed stability requirements.
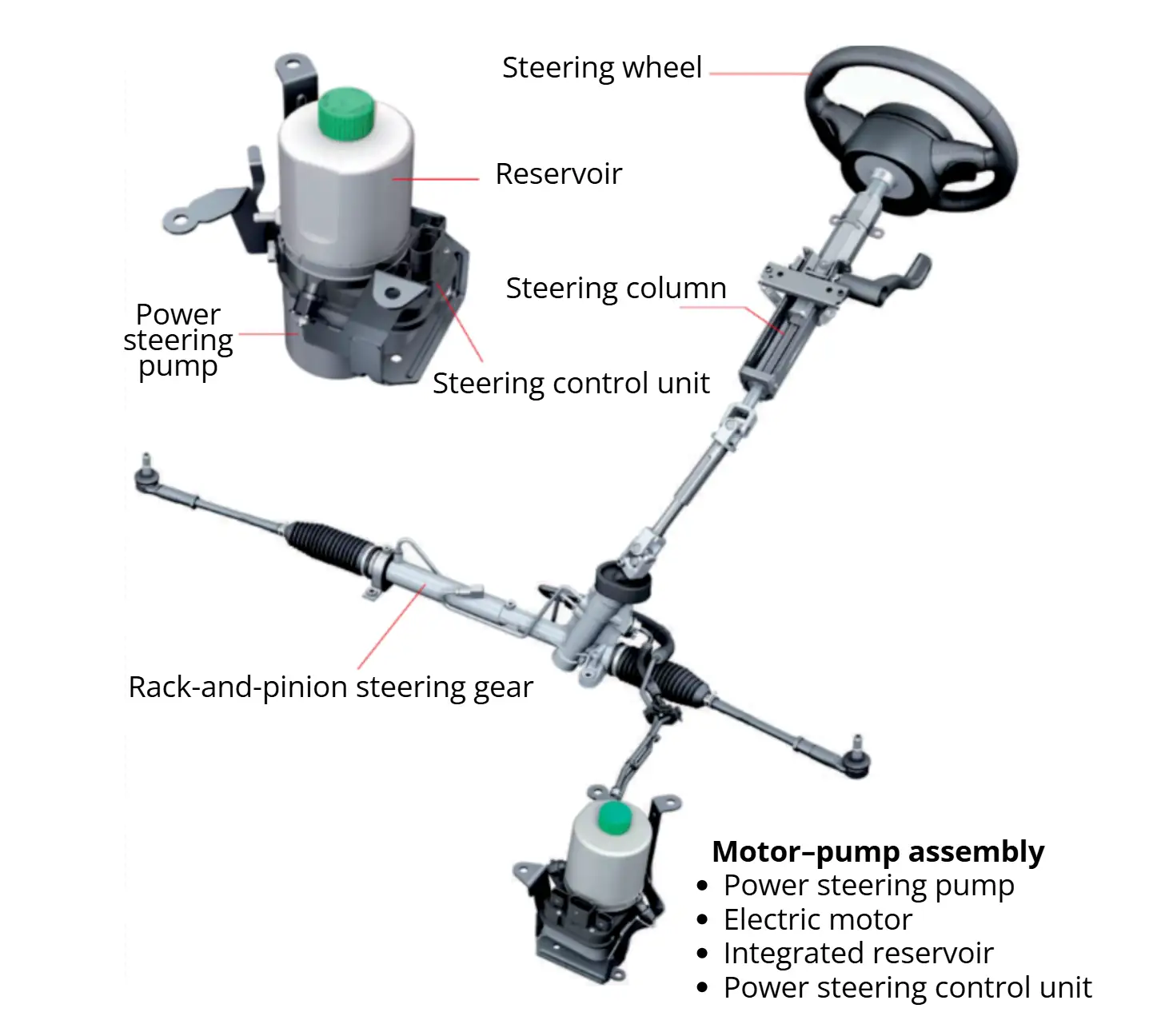

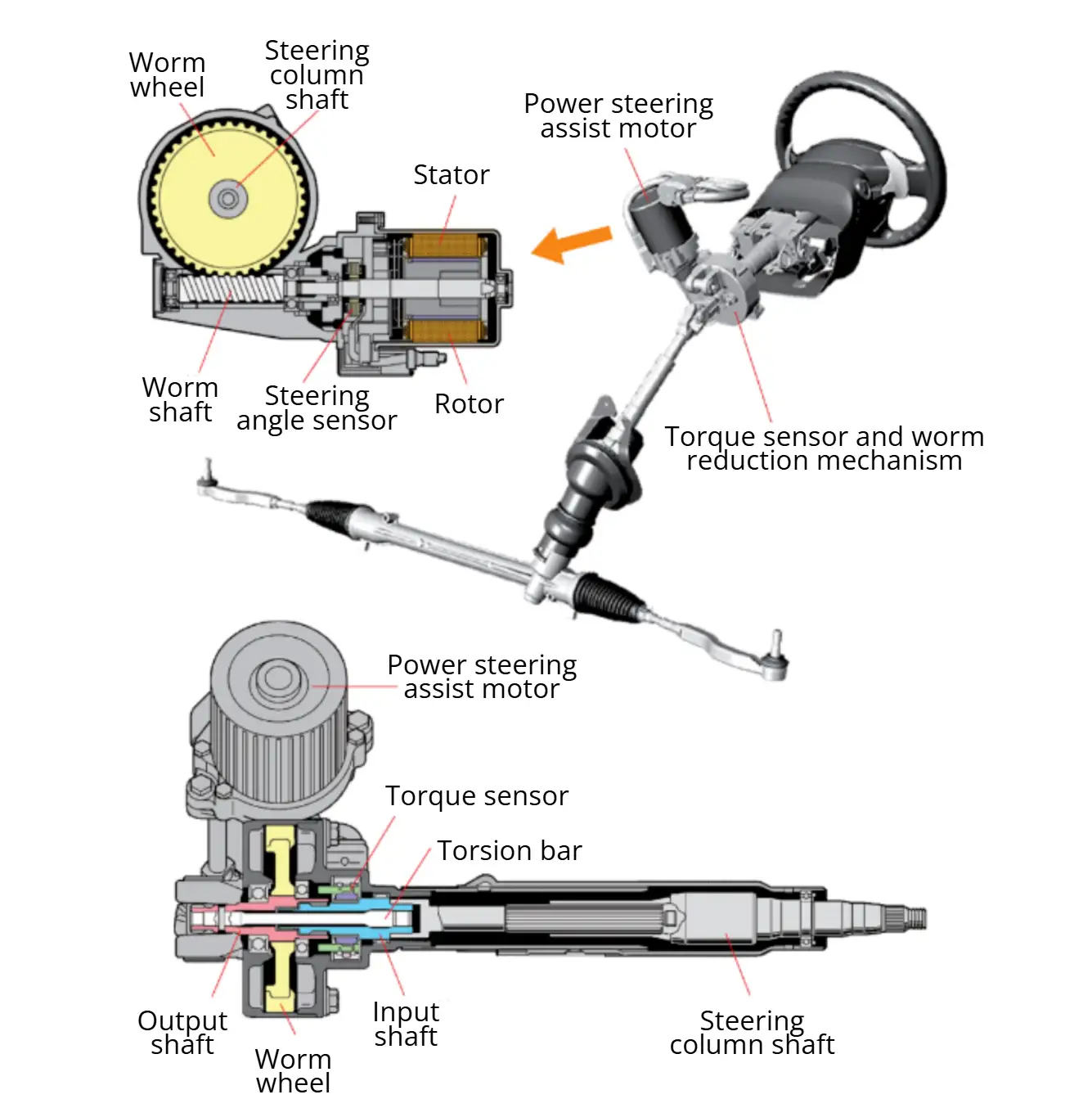
2.4 Electric Power Steering (EPS)
Electric Power Steering (EPS) uses an electric motor to provide steering assist, applying torque to either the steering column or the steering rack. A gear reduction mechanism typically connects the motor to the steering components.
- A torque sensor measures steering torque and direction.
- The ECU calculates required assist based on torque, steering direction, and vehicle speed.
- The motor outputs a corresponding torque to provide steering assistance.
EPS assistance varies with steering torque, vehicle speed, and steering angle. With automated parking systems, the EPS motor can also control steering automatically.
Characteristics:
- Low-speed steering: High assist for light steering effort
- High-speed steering: Lower assist for better road feel and vehicle stability
Most EPS systems offer selectable steering modes (Comfort, Standard, Sport) with different assist curves.
EPS assistance varies with steering torque, vehicle speed, and steering angle. With automated parking systems, the EPS motor can also control steering automatically.
Characteristics:
- Low-speed steering: High assist for light steering effort
- High-speed steering: Lower assist for better road feel and vehicle stability
Most EPS systems offer selectable steering modes (Comfort, Standard, Sport) with different assist curves.
EPS can be categorized by motor placement:
2.4.1 C-EPS (Column EPS)
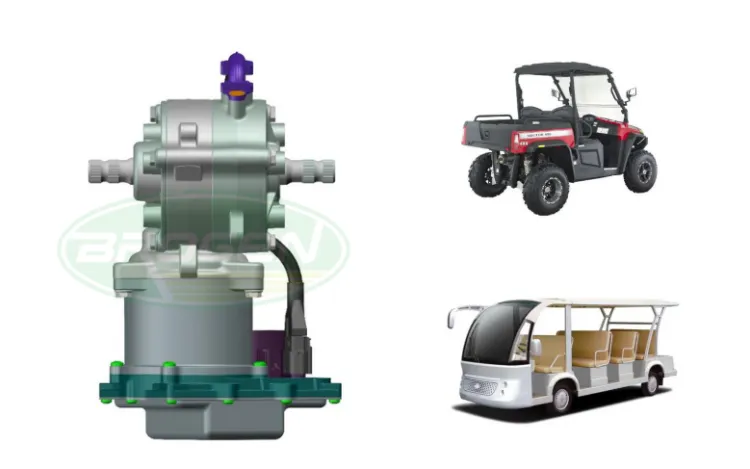

The motor is mounted on the steering column.
- Advantages: Compact structure; suitable for small vehicles with low assist demand.
- Disadvantages: Motor vibration may directly affect steering feel; closer to the cabin → higher noise intrusion.
2.4.2 P-EPS (Pinon EPS)
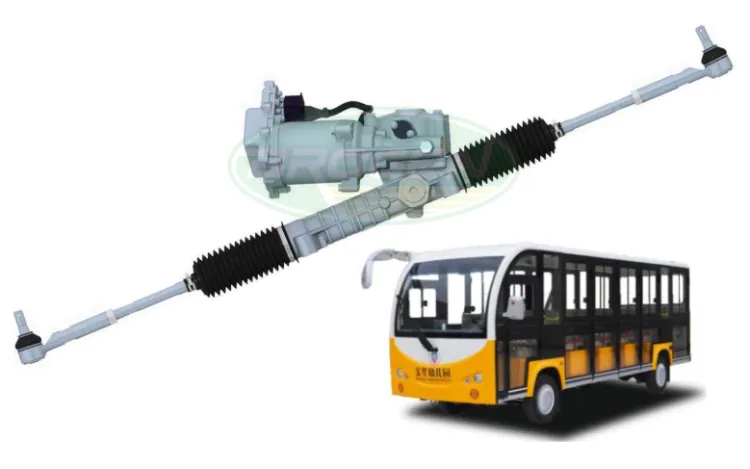

The motor is mounted on the pinion of the steering gear.
- Advantages: Compact; suitable for small vehicles.
- Disadvantages: Similar to C-EPS, motor interference may affect steering feel.
2.4.3 DP-EPS (Pinon EPS)
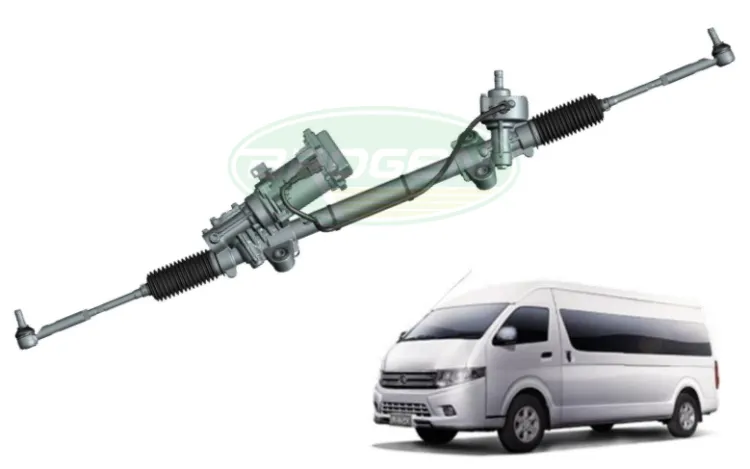

Adds an additional motor-driven pinion shaft.
- Advantages: Better noise performance; provides higher assist; motor acts on the rack → reduced sensitivity to torque ripple; suitable for mid-to-high-end vehicles
- Disadvantages: Higher cost
2.4.4 R-EPS (Pack EPS)
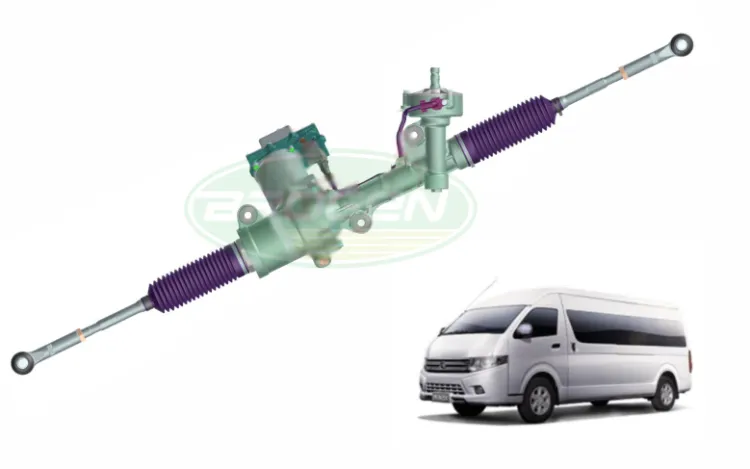

Uses a more precise ball-screw assist mechanism. Its operating principle is as follows: when the electric motor rotates, it drives the ball-nut through a belt pulley. As the ball-nut rotates, the recirculating balls inside convert this rotation into linear motion, moving the rack shaft left or right.
- Advantages: high efficiency; capable of large assist torque; commonly used in MPVs, commercial vehicles, and premium cars.
3. Brogen Power Steering Systems
At Brogen, we offer a comprehensive range of power steering solutions for commercial vehicles, including EPS, EHPS pumps, EH-RCB, and eRCB systems, which support various vehicle types and performance requirements.
- Learn more here: https://brogenevsolution.com/electric-power-steering-solutions/
- Business inquiry: contact@BrogenEVSolution.com
Contact Us
Get in touch with us by sending us an email, using the Whatsapp number below, or filling in the form below. We usually reply within 2 business days.
Email: contact@brogenevsolution.com
Respond within 1 business day
Whatsapp: +8619352173376
Business hours: 9 am to 6 pm, GMT+8, Mon. to Fri.
LinkedIn channel
Follow us for regular updates >
YouTube channel
Ev systems introduction & industry insights >