Understanding Electric Power Steering Solutions: Types and Key Differences
The power steering system is a crucial component of a vehicle, serving as an important connection between the driver and the car. It has evolved alongside the overall development of vehicles and the emergence of new technologies. Initially, there was mechanical steering, followed by hydraulic power steering systems (HPS), electro-hydraulic power steering systems (EHPS), electric power steering systems (EPS), and now the latest steer-by-wire (SBW) technology.
Depending on the location of the assist motor, electric power steering systems (EPS) are classified into C-EPS, P-EPS, DP-EPS, and R-EPS. Each type has its own unique functional and performance characteristics.
Different Types of Electric Power Steering Systems
1. Column Assist Type Electric Power Steering (C-EPS)
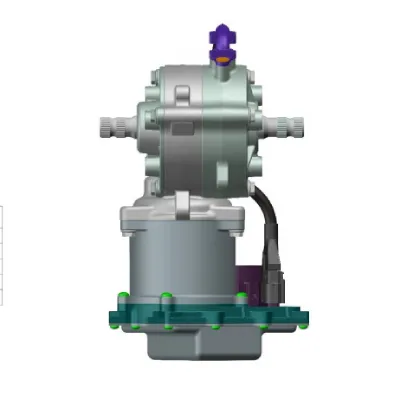

- Motor placement: the motor and reduction gears are mounted on the steering column. The motor’s torque works together with the driver’s input to rotate the steering column, which then transmits force through the intermediate shaft and pinion to the rack, providing steering assistance.
- Applicable vehicle types: particularly suitable for compact vehicles that do not require excessive assistance.
- Structural characteristics: compact design, easy installation, and minimal required installation space.
- Driving experience: lightweight steering at low speeds, stable handling at high speeds, and excellent self-centering performance.
- Additional features: equipped with self-diagnosis and safety control functions, highly adaptable, allowing for customization of electric power steering columns and controllers based on different vehicle models.
2. Pinion Assist Type Electric Power Steering (P-EPS)

- Motor placement: the motor provides assistance directly to the pinion of the rack-and-pinion steering system, combining the precise adjustability of electric power steering with the strong road feedback typical of hydraulic power steering.
- System performance: equipped with a waterproof, compact, lightweight, high-performance integrated motor-ECU unit, the system delivers high rigidity and excellent dynamic steering performance.
- Structural characteristics: the compact, integrated housing structure enhances the precision of component manufacturing and improves overall product reliability.
- Cost: P-EPS is more expensive compared to C-EPS.
3. Dual-Pinion Assist Type Electric Power Steering (DP-EPS)
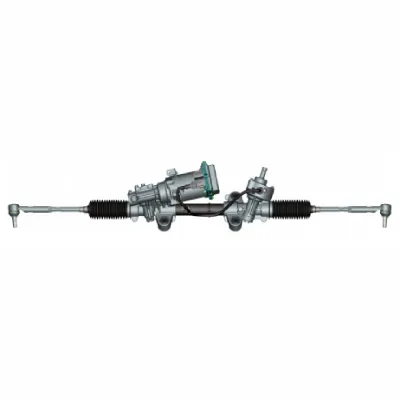

- Motor placement: an additional assist motor is placed on another part of the rack, applying steering force to the tie rod via a pinion. Together with the pinion on the intermediate shaft and tie rod, this forms a dual pinion structure.
- Applicable vehicle types: suitable for mid-size SUVs, large SUVs, MPVs, pickups, and other passenger vehicles, meeting the requirements for ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems).
- Performance advantages: the servo motor only operates when steering assistance is needed, reducing fuel consumption by 3-5%. It complies with ISO 26262 functional safety standards at the ASIL D level. The system is designed with high robustness to handle complex driving conditions, with high steering precision to support driving assistance at high speeds.
- Redundant design: the fully redundant DP-EPS system includes redundancy in power supply, communication, sensors, electronic control, and motor output, significantly enhancing the reliability and safety of the system.
4. Rack Assist Type Electric Power Steering (R-EPS)
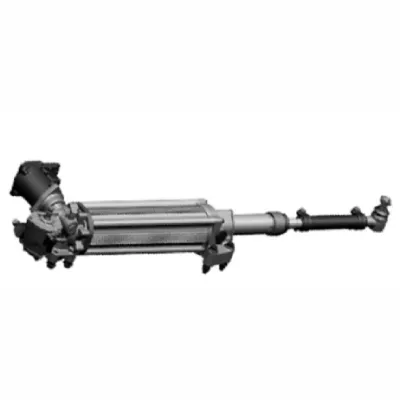

- Motor placement: the motor typically applies force to the rack through a timing belt or ball screw. In some configurations, a coaxial motor directly provides assistance via a roller screw.
- Structural characteristics: the structure is relatively compact, making it suitable for scenarios where front axle loads are increasing and the steering system is positioned farther from the driver.
- Driving experience: it offers an enhanced steering feel and higher efficiency, making it more suitable for premium vehicles.
- Performance advantages: with a finely tuned steering feel and excellent NVH performance, it fully meets the steering needs of vehicles ranging from mid-size sedans to luxury MPVs. It also supports Level 2+ autonomous driving, including features like Lane Keep Assist (LKA), Automated Parking Assist (APA), and Remote Control Steering (RCS).
- Safety: the entire product platform is developed following ISO 26262 processes, ensuring functional safety at ASIL-D level.
Key Differences of Electric Power Steering Systems
After gaining a basic understanding of the different EPS structures, let’s take a look at the performance differences and suitable applications for each type:
1. Assist Effect and Applicable Vehicle Types
| EPS Type | Maximum Assist Force | Applicable Vehicle Types |
|---|---|---|
| C-EPS | 11 kN | Compact cars, small SUVs |
| P-EPS | 12 kN | Midsize cars, SUVs |
| DP-EPS | 13 kN | Midsize/large SUVs, MPVs, pickups |
| R-EPS | 16 kN | Luxury cars, large SUVs, performance vehicles |
C-EPS, with its compact structure, is typically used for vehicles that require moderate steering assistance. P-EPS, by applying assist force to the pinion, provides stronger assistance and is suitable for heavier vehicles. DP-EPS, with its dual-pinion design, offers even greater assist force to meet the needs of larger vehicles. R-EPS generally delivers the strongest assist, making it ideal for luxury and performance vehicles.
2. Energy Consumption and Efficiency by EPS Type
| EPS Type | Energy Consumption | Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| C-EPS | Low | Moderate |
| P-EPS | Moderate | Relatively High |
| DP-EPS | Moderate to High | High |
| R-EPS | High (operates only when needed) | Very High |
While DP-EPS and R-EPS have relatively higher energy consumption, their servo motors only operate when steering assistance is required, effectively reducing fuel consumption in real-world use. Additionally, these systems generally exhibit higher efficiency, converting electrical energy into steering assistance more effectively.
3. Response Speed and Precision by EPS Type
| EPS Type | Response Speed | Precision |
|---|---|---|
| C-EPS | Moderate | Moderate |
| P-EPS | Relatively Fast | High |
| DP-EPS | Fast | High |
| R-EPS | Very Fast | Very High |
R-EPS typically exhibits the fastest response speed and highest precision, thanks to its advanced control algorithms and precise mechanical structure. DP-EPS also performs well, while C-EPS and P-EPS are comparatively slower and less precise.
4. Noise Levels and NVH Performance by EPS Type
| EPS Type | Noise Level | NVH Performance |
|---|---|---|
| C-EPS | Moderate | Moderate |
| P-EPS | Lower | High |
| DP-EPS | Very Low | High |
| R-EPS | Very Low | Very High |
Among these types, only C-EPS has the motor located in the passenger cabin, making it the noisiest and has the worst NVH experience. In contrast, P-EPS, DP-EPS, and R-EPS have their motors in the front compartment, resulting in better noise performance. Additionally, R-EPS benefits from its force transmission structure, offering the best NVH performance.
5. Redundancy Design and Safety by EPS Type
| EPS Type | Redundancy Design | Safety Level |
|---|---|---|
| C-EPS | Minimal | Moderate |
| P-EPS | Limited | High |
| DP-EPS | High (Fully Redundant) | Very High |
| R-EPS | High (in some models) | Very High |
DP-EPS typically features a fully redundant design, ensuring that the system can maintain steering assistance even in the event of a single-point failure, significantly enhancing safety. R-EPS also incorporates redundancy in certain high-end models, while C-EPS and P-EPS have relatively limited redundancy.
6. Supported Levels of Autonomous Driving by EPS Type
| EPS Type | Supported Autonomous Driving Level |
|---|---|
| C-EPS | L0-L1 |
| P-EPS | L1-L2 |
| DP-EPS | L2-L3 |
| R-EPS | L3-L4 |
As autonomous driving technology continues to evolve, EPS systems are enhancing their performance and capabilities. Due to their robust performance and redundancy design, DP-EPS and R-EPS are typically capable of supporting higher levels of autonomous driving.
Conclusion
C-EPS currently dominates the passenger car market due to its clear cost advantages. However, in recent years, the market share of DP-EPS and R-EPS has been rapidly increasing for several reasons:
The accelerated penetration of electric vehicles has raised the steering assistance requirements due to the greater overall vehicle weight.
The rapid adoption of advanced driver assistance features has necessitated redundancy designs and fully powered steering systems, prompting more vehicle models to integrate DP-EPS or R-EPS.
The increase in mid-to-high-end models has led to higher expectations for steering performance and user experience.
Brogen Electric Power Steering Systems
At Brogen, we offer an extensive portfolio of electric power steering systems, including C-EPS, P-EPS, P-SBW, DP-EPS, and R-EPS, designed for a variety of vehicles such as passenger cars, vans, AGVs, golf carts, buses, and trucks. Our R&D team features core specialists with experience in designing and developing steering and suspension systems for leading manufacturers, including Toyota, Mitsubishi, Lexus, and Honda. Our electric power steering factory boasts a high production capacity, capable of producing up to 1 million sets of power steering systems annually.
Contact Us
Get in touch with us by sending us an email, using the Whatsapp number below, or filling in the form below. We usually reply within 2 business days.
Email: contact@brogenevsolution.com
Respond within 1 business day
Whatsapp: +8619352173376
Business hours: 9 am to 6 pm, GMT+8, Mon. to Fri.
LinkedIn channel
Follow us for regular updates >
YouTube channel
Ev systems introduction & industry insights >